Medicare is a fantastic benefit that makes it possible for many retirees to enjoy life more fully, thanks to premiums that are far more affordable than market rates on private health insurance plans. Still, Medicare isn’t free, and there are some sneaky extra costs that can blindside you if your income rises above a certain threshold.
Friends, meet IRMAA.
Just as a sudden windfall or boost in your retirement income can bump you into a higher tax bracket, so too can it push you into a higher payment tier for your Medicare Part B and Part D coverage.
Fortunately, unplanned IRMAA expenses can be avoided with careful planning. Here’s what you need to know.
Understanding IRMAA
IRMAA stands for the Income Related Monthly Adjustment Amount that is added to some people’s Medicare premiums. While most people who receive Medicare benefits when they reach age 65 will never have to worry about IRMAA, those with higher incomes are charged extra each month for their coverage.
IRMAA charges affect premiums for Medicare Part B (medical insurance) and Part D (prescription drug coverage) plans. If you have a Medicare Advantage plan, you will also be subject to IRMAA charges on the affected portions of the plan.
IRMAA charges are based on your yearly income as reported on your tax return. Specifically, the Social Security Administration (SSA) uses your Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI) for its calculations.
For this year, anyone earning less than $88,000 filing single or $176,000 filing joint will not have an IRMAA charge: your monthly premium is the standard $148.50 per person, per month.
However, if you earn more than that, you will be charged extra based on your income bracket:
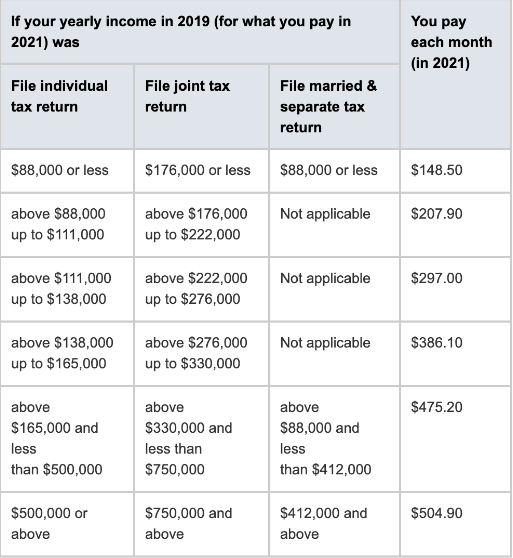
Souce: medicare.gov
Likewise, you will also be charged extra for Part D coverage, following the same income brackets:
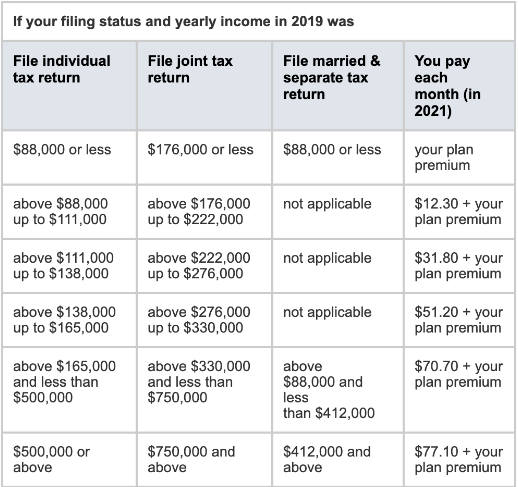
Source: medicare.gov
Why IRMAA Can Be Tricky
When the SSA determines your IRMAA charges, they use your MAGI from two years prior to the year in question. For example, premiums for 2021 are based on the income from your 2019 tax return.
This means that decisions you make could come back to haunt you in the future.
For example, if you sell some real estate and earn a profit, that money could push your income into a higher tax bracket and a higher IRMAA bracket. While you’ll pay income taxes on the proceeds relatively quickly, the IRMAA charges will be delayed, which leaves you open to a budget shortfall if you’re caught off-guard.
The income thresholds for IRMAA brackets are also subject to change each year, making it harder to plan ahead. That’s because IRMAA thresholds are no longer frozen but instead tied to inflation using the Consumer Price Index. You can make an educated guess about next year’s premiums and IRMAA thresholds before official numbers are published, but you’ll want to pad this number to avoid an unpleasant surprise.
Finally, major life events can have a big impact on your income, and this can in turn affect your IRMAA charges in the future. Fortunately, the SSA will consider an appeal if your circumstances have changed and your income is significantly lower than it was in the tax year used for your determination. Not everything that impacts your income is officially recognized, but these events could help your appeal:
- Death of a spouse
- Divorce or annulment
- Loss or reduction of a pension
- Loss of property that generates income
- Marriage
- Settlement payments from an employer
- Unemployment or reduced hours/income
Tips for Avoiding an IRMAA Charge
In general, the best way to avoid unwanted IRMAA charges is to make sure your income remains steady throughout retirement. This means remaining just as vigilant about your IRMAA bracket as you are about your marginal tax rates. This is especially important if your income hovers near the top of your current bracket, as you will have less room for error.
Some common income-boosters to be aware of include:
- Selling real estate, especially if you’ve owned it for a long time and it has significantly increased in value.
- Selling investments subject to capital gains taxes. These transactions typically occur outside of your IRA or 401(k) in brokerage accounts.
- Converting a traditional IRA to a Roth, which leaves you open to a big tax liability and IRMAA charges on the lump sum, which is considered income.
Another common income-booster comes when you turn 72 and must take required minimum distributions (RMD) from a traditional IRA or 401(k). If you plan carefully, you can reduce other portions of your income so this balances out, or you can consider giving your RMD to charity if you itemize deductions.
Feeling a little dizzy from all the things you have to keep track of in retirement? We’re here to help! A solid financial plan will take into account all of your investments, income streams, and expenses like taxes and IRMAA so you can enjoy the retirement you deserve. Get in touch today to learn more.
One of the biggest expenses in your life is federal income tax. Sure, writing the check for the payment on your home is a major milestone, but most people will end up paying far more than that in taxes over the course of a lifetime.
And yet, you’re probably not paying as much as you think.
You read that correctly! One of the biggest misconceptions people have about their taxes surrounds their tax rates and how they work. And this misunderstanding leads most people to think they owe more than they actually do.
The trouble comes from a complex tax code that uses tax margins to tax different levels of income at different rates. Understanding exactly how this works is crucial for making good decisions about your money.
So let’s clear up the misconceptions and misunderstandings. Here’s what you need to know.
What Is Your Marginal Rate?
Tax margins are the result of a progressive tax system, in which people with lower income pay taxes at a lower rate, while people with higher incomes are charged more. Higher tax rates kick in when you cross a certain income threshold, creating what we call tax brackets:
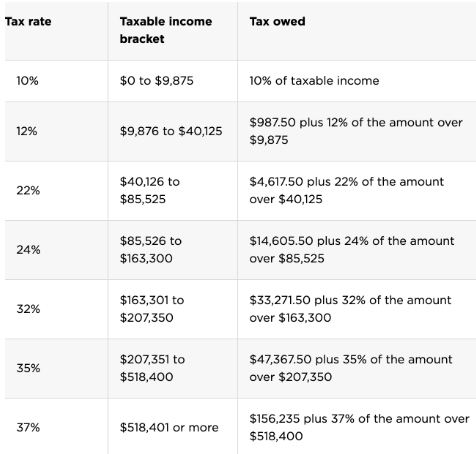
Single Filer 2020 Federal Income Tax Brackets
Source: NerdWallet
Let’s look at an example. If a single person earned $45,000 of taxable income in 2020, they’d be in the 22% tax bracket.
But that does not mean they pay 22% in income taxes.
In reality, they only pay 22% tax on part of their income — specifically, the part that kicks them over the $40,125 limit of the 12% bracket.
The best way to understand this is to imagine each tax bracket like a bucket. Everyone’s income is first poured into the 10% tax bucket. But that bucket only holds $9,875. If your taxable income is less than that, then you’re done — you only owe 10% in taxes.
But if your taxable income is more than $9,875, it will spill over into the next bucket. This is the 12% bucket. This bucket holds up to $40,125, so our sample tax payer above has income that will also spill into the third bucket. But the 22% bucket is where he stops, because it holds more than $48,000.
Our taxpayer will pay the taxes on each bucket, meaning he will pay 10% on the $9,875 in the first bucket, 12% on the $30,250 in that bucket, and 22% on the rest — but that 22% bucket only has $4,875 in it.
So while this taxpayer has a marginal tax rate of 22% — the highest bracket he falls into — he won’t pay 22% on all of his money. His effective tax rate is actually lower.
What Is Your Effective Tax Rate?
Your effective tax rate is the percentage of your income that you actually pay in taxes — and this is almost always less than your marginal rate. This is much easier to calculate: just take the total dollar amount you pay in income tax and divide it by your total income.
To see how it works, let’s calculate the effective tax rate for our sample taxpayer. He paid:
- 10% on $9,875 = $987.50
- 12% on $30,250 = $3,630.00
- 22% on $4,875 = $1,072.50
That’s a total of $5,690 in income tax. That means his effective tax rate is:
- $5,690 ÷ $45,000 = 0.126, or 12.6%
As you can see, our sample taxpayer doesn’t pay anywhere near 22% on his income — his effective tax rate is only 12.6%.
This is great news, and it should hopefully lay to rest the myth that being pushed into a higher tax bracket suddenly takes all your money away, or that you could actually end up owing all the extra money you earn, making it somehow not worth getting a raise. This is simply not true.
Using Your Marginal and Effective Tax Rates to Make Good Decisions
Your effective tax rate is a snapshot of your total tax burden, which can be useful in monthly and yearly budgeting. For example, freelancers and other workers with 1099 income with no tax withholding can use their effective tax rate to plan ahead and avoid a shock when their tax bills are due in April. The same is true for retirees who want to have a clear understanding of what they’ll owe on their IRA distributions.
Your marginal tax rate, on the other hand, is important for making strategic retirement decisions. That’s because any additional tax deferred retirement account (IRA, 401k, 403b, TSP, 457) income you withdraw will be taxed at your marginal rate — that is, your current “bucket” that you’ve worked your way up to. If you have flexibility about taking a distribution now or later, using your marginal rate to compare options will give you a more accurate view of what those changes will cost and can help you save money in the long run.
It should be noted that these calculations can get complicated. For example, you might want to figure your state taxes into your effective tax rate, or you may need help calculating an accurate marginal tax rate if some of your strategies push you into a higher bracket. We’re here to help! Tax planning is a crucial part of financial planning, so please get in touch if you have additional questions about how your marginal and effective tax rates impact your retirement plan.
Believe it or not, 2020 is — finally! — over, and it’s almost time to file your taxes for this very strange year. Are you ready?
As you gather your paperwork to do your taxes, there’s some great news for Arizona residents: the state offers four big tax credits that you still have time to take advantage of. Each Arizona tax credit is tied to charitable giving, so you get to feel good about your contributions and save money on your taxes at the same time.
Here’s what you need to know to use these credits to lower your 2020 state tax bill.
Tax Credits Vs. Tax Deductions
For federal income taxes, you’re allowed to claim a tax deduction for charitable giving if you itemize deductions. For 2020, there’s also a special rule allowing you to deduct up to $300 of charitable contribution even if you don’t itemize. This was designed as an incentive for more people to support charities hurting during the pandemic.
When you take a tax deduction for charitable giving, the amount you give is subtracted from your taxable income. This reduces the total amount of tax you owe. For example, if you donate $100 to Big Brothers Big Sisters and your total tax rate was 12%, you save a total of $12 on your tax bill.
When you take a tax credit for charitable giving, the amount you give is subtracted from the total tax you owe. In this situation, that $100 donation will save you $100 on your tax bill. For Arizona residents who take advantage of special tax credits, that’s like getting some free money to give to charities: instead of paying it to the state government, you instead can choose to give it directly to a group whose work you believe in and want to support.
Rules for Claiming Arizona Tax Credits for Donations
There are four major tax credits that you can use to offset certain charitable donations in Arizona. For all of them, you have until April 15, 2021 — or until the date you file your return, if you do so early — to donate for the 2020 tax year. That means you can still donate and get the credit if you haven’t already!
To claim the credit, you’ll need to make sure donations go to a qualified organization. Each of the four credits has a maximum eligible amount as well. You can always give more, but your tax credit will be capped at the maximum.
Qualified Charitable Organization (QCO) Credit
The QCO Credit is available for donations to qualified charities that serve the needs of low-income families struggling to fulfill their basic needs for food, shelter and healthcare. There are hundreds of Arizona-based organizations to choose from.
Use this list to check eligibility and to find the QCO Code you’ll need to complete your tax forms.
- Maximum Credit: $400 single/$800 married filing jointly
- Paperwork: Tax Credit Form 321
Qualified Foster Care Organization (QFCO) Credit
The QFCO Credit is very similar to the QCO credit, but is carved out specifically for charities that support children in foster care. The credit has more generous limits, but there are far fewer organizations that qualify.
Use this list to check eligibility and to find the QFCO Code you’ll need to complete your tax forms.
- Maximum Credit: $500 single/$1,000 married filing jointly
- Paperwork: Tax Credit Form 352
Private School Credit
The Private School Credit is available for donations to a Private School Tuition Organization. These groups provide scholarships for needy students to attend private schools in Arizona. This tax credit is actually two separate credits; the amount you donate will determine whether you need to apply for one or both credits when you file your taxes.
Use this list to check school eligibility.
- Maximum Credit: $1,183 single/$2,365 married filing jointly
- Paperwork: Tax Credit Form 323 for the first $593 single/$1,186 married filing jointly; Tax Credit Form 348 for the next $590 single/$1,179 married filing jointly
Public School Credit
The Public School Credit is available for donations to Arizona public or charter schools in support of eligible activities and programs. It’s also available to families who have directly paid fees to a school for these activities.
Use this list to check school eligibility; use this webpage to see which activities and programs are eligible.
- Maximum Credit: $200 single/$400 married filing jointly
- Paperwork: Tax Credit Form 322
The Bottom Line
Giving to charities is always worthwhile. It makes you feel good, and it helps people and organizations in need. And if you can earn a little reward for your efforts in the form of a tax credit, even better! As you plan for this year’s taxes, remember that it’s not too late to donate to an Arizona school or charity to take advantage of a tax credit for 2020.
When it comes to retirement planning, one of the biggest choices you’ll face is whether to choose a traditional or a Roth IRA. They each have their own distinct advantages, but the right one for you will depend on your unique circumstances.
Unhappy with your original choice? The good news is that you can convert a traditional IRA into a Roth. The bad news? It might be too costly to be worth it. Here’s what you need to know.
Roth IRAs vs. Traditional IRAs
Before going any further, let’s review the basic difference between a traditional and a Roth IRA. Both of these individual retirement funds are tax advantaged to help you grow your nest egg faster than you would in a plain old brokerage account. The major difference is in when you realize the tax savings.
With a traditional IRA, your contributions are not taxed, which means you can deduct all the money you contribute from your income in that tax year. This can lower your taxable income and save you money upfront. The catch? You’ll pay taxes on the money when you take distributions during retirement. Once you start using the money, it will be taxed at your regular rate during retirement.
With a Roth IRA, your contributions are taxed along with the rest of your income each year — but you’ll never pay taxes on it again. The money grows tax-free until you need it at retirement, when you can enjoy tax-free distributions.
Roth IRAs are obviously appealing to anyone who doesn’t want to worry about taxes in their retirement, but they have a few other advantages as well:
- Ability to withdraw contributions at any time: Because you already paid taxes on this money, you can withdraw the amount of your original contributions at any time without penalty, which can be handy in an emergency — even before the magic age of 59½.
- No required minimum distribution (RMD): While a traditional IRA forces you to start taking distributions by age 72, you can keep growing your money in a Roth IRA for as long as you like — good news for anyone who plans to live a long life!
- Tax-free inheritance for your heirs: If you die with money left in your Roth IRA, your heirs will also enjoy tax-free distributions, which they can take over a five-year period.
What Is a Roth Conversion?
If you’re thinking to yourself that a Roth IRA sounds pretty great, you’re not alone. Many people want to make the switch from a traditional IRA to a Roth — if not for all, then for at least some of their retirement savings.
This can be done via a Roth conversion. A Roth conversion transfers funds from your traditional IRA into a Roth. To do this, you’ll need to pay taxes on the money that you convert — taxes that will be charged at your regular income tax rate when your tax bill is due on April 15.
That sticking point can be enough to stop many people in their tracks, especially if they don’t have the cash on hand to pay that big tax bill. But for some, a Roth conversion is a good choice.
Is a Roth Conversion Right for You? 4 Questions to Ask Yourself
1. Will Your Future Tax Bracket Be Higher Than Your Current One?
This is the hardest question to answer, but getting it right is key. If you will be in a higher tax bracket when you retire than you were when you contributed to your IRA, a Roth IRA will save you money. But how can you know?
This takes careful planning, with research about your projected income over your lifetime and some honest answers about your potential for career growth. Most people earn more at the end of their careers than they do in the beginning, but how much will you need or want during your retirement? If your home is paid off and your children launched, you may be able to live nicely on less. But that means that a Roth IRA won’t save you any money at all, because you’ll have paid taxes at a higher rate back when you earned the money.
The other big unknown is the state of the tax code. Do you think taxes will go up in the future? If so, a Roth conversion can help you take advantage of today’s lower rates.
2. Can You Afford the Conversion Taxes Today?
Remember, you will owe income taxes on the full amount of money you convert into a Roth IRA in the year you make the conversion. So if you’d like to convert $50,000, can you pay 22% of that in taxes — or even more, depending on your tax bracket? That can be a big chunk of change, and you’ll need it in liquid assets that you can tap into from another account.
3. Do You Want to Pay the Taxes?
If your finances allow you to pay the taxes, think again: do you want to? What are your goals for opening a Roth IRA? If you have extra money lying around and aren’t worried about paying it to Uncle Sam, great. If you have debt, or are less certain about your future, converting to a Roth could be a gamble that’s not worth it. Even if you’re secure, you may find that traveling, charitable work, or even spending the money on your family now instead of building an inheritance vehicle feel like better uses of the money. Explore your feelings about the money as you work to crunch the numbers.
4. How Long Until You Need the Money for Retirement?
Roth rules require you to hold the account for five years until you make penalty-free withdrawals of the earnings, so plan carefully. Will you need this money before that period is up, or do you have time? If you plan to use the money right away, a conversion isn’t your best move.
Still uncertain about whether converting to a Roth IRA is a good move? We’re here to help! We’ll walk you through your options, help you calculate your tax burden, and figure out how to structure a conversion if the numbers are in your favor. We can structure a partial conversion or spread it out over time to ensure that you can afford the taxes and don’t accidentally push yourself into a higher income bracket by mistake. Roth conversions are complex, so contact us today for expert guidance.
Retirement planning is tricky. On one hand, you want to make sure you save enough to enjoy yourself for a long, happy life once you stop working — and that could mean that you need decades of secure income. On the other hand, you also have dreams and obligations right now, and you need to balance your savings goals with real life.
Add to that all the moving parts of retirement planning — Social Security, stock market changes, inflation, and taxes — and you can be forgiven if your head is spinning.
But we’re here to help.
One important issue that many people don’t think about until it’s too late? The Social Security earnings test. Depending on when you choose to retire, your income could be limited. Here’s what you need to know to make the most of your social security payouts.
Social Security Basics
If you haven’t given much thought to Social Security, it’s worth taking a moment to remind yourself of what you’re entitled to. Social Security retirement benefits cover any American who has earned enough work credits by paying Social Security taxes for roughly 10 years over their lifetime. The amount of retirement benefits you can receive is based on a percentage of the total you’ve paid into the system over the years, though this amount varies depending on your age when you choose to retire and begin collecting.
You can begin receiving benefits as young as age 62, though this will result in a reduced monthly payout for the rest of your life. Full retirement age is anywhere from 66 to 67, depending on when you were born. And if you can wait even longer, your benefits will continue to increase until age 70. Your monthly benefit at age 70 could be nearly double what it is at age 62, so it’s important to use a Social Security calculator to understand how your retirement age will affect your income.
But What if You Keep Working?
For many people, working is a passion that they don’t intend to give up. For others, additional income in their sixties and seventies will be crucial to helping them meet their retirement goals. But choosing to work once you collect Social Security can impact your payments: Work too much, and your Social Security check could be much smaller than you anticipated, throwing a wrench into your retirement income and leaving you short on cash for living expenses.
The Social Security Earnings Test
To prevent people from depleting the Social Security system while still working, the law limits the benefits people are entitled to if they retire early — that is, before their full retirement age (whether that’s 66 or 67). So if you pick up an extra job after you reach full retirement age, you will still earn your full Social Security benefits on top of your extra earned income.
But if you choose to collect Social Security before your full retirement age, you’re subject to the earnings limit. Each year, the earnings limit rises to account for inflation. In 2020, the income limit is $18,240. This means that if you are not at the full retirement age, you can earn up to $18,240 and still get your full benefits. Go over that amount, and the SSA reduces your benefits.
The calculations for reduced benefits are complex. If you will not reach your full retirement age in 2020, and you earn more than $18,240, your benefits will be reduced by $1 for every $2 over the limit you go. If you will reach full retirement age in 2020, you’ll lose $1 for every $3 over the limit you go.
There is also a special rule about the year in which you retire: Your earnings test only begins in the months you have collected Social Security, so that all of your pre-retirement work income doesn’t count against you for the limit. For example, if you retire from a lucrative career in July and then take a part-time job in August, you can receive your full benefits as long as your monthly earnings aren’t more than 1/12 of $18,240 ($1520 per month).
Tips for Working Around the Earnings Penalty
If you’re confused, you’re certainly not the first! This is a complex formula, and it’s definitely a good idea to run a few scenarios on the Earnings Test calculator to see how excess earnings could affect your benefits.
There are also some tried-and-true tactics for avoiding a nasty surprise when you open your Social Security check:
- Hold off on collecting Social Security until you reach full retirement age (FRA). This allows you to completely avoid the earnings test and any penalty, as it only applies to people below FRA.
- Consider withdrawing your Social Security application. If you’ve already applied for benefits but have changed your mind now that you know more about the earnings limit, you can withdraw your application within 12 months of submission. You can apply for benefits again later — ideally when you’re closer to FRA.
- Track your income carefully. If you want to —or have to — work, track your hours to try to stay within the earnings limit if you can. If you need to cut back near the end of the year to avoid going over the limit, it may make sense to do so.
- Consider other retirement income instead of working. If you have investments that can replace the income from extra work before you reach FRA, it might make sense to use those instead. For example, you can pull principal from a Roth IRA with no penalty at any age.
- Plan ahead! Working with an advisor who can run through every scenario will give you peace of mind and help you come up with a plan that maximizes your Social Security while preserving your retirement savings for the long haul.
Need help getting started? Weighing the pros and cons of working through retirement is a big question, and we’ve got answers. Contact us today to set up a consultation to get a clear view of your personal retirement plan.
For many people, thinking about retirement is a double-edged sword. On one hand, it’s exciting to contemplate the freedom that comes when you stop working for full time and can devote yourself to projects, travel or spending time with loved ones. On the other hand, retirement planning can be incredibly stressful — especially if you started to save later in life or are concerned that you won’t have enough income to live the life you’ve always dreamed of.
So how, exactly, should you plan your retirement income? There are four reliable strategies that work for most people. Understanding these income strategies is a good first step in laying out your future income so that you can live a worry-free retired life.
1. The Systematic Withdrawal Strategy
Systematic withdrawal is probably the most common retirement income strategy. After many years of depositing money into your retirement account, you finally begin to take it out again. This is, however, more complex than just adding and subtracting cash from a savings account.
When you add money to an IRA or 401(k), it is used to purchase a variety of investment products, including mutual funds, bonds, CDs, stocks, and more. Each of these items fluctuates in value over time. When you take money out of your retirement account, you end up selling off a portion of these investments, cashing out of your stocks and bonds.
As you do so, you’ll have a bit less principal in your account to continue earning money, so a systematic withdrawal strategy must take into account both how much money you need and also how many years you will need it for to ensure your income lasts.
Pros: Having a well-rounded portfolio lets you continue to earn money in the long term even as you begin to sell off stocks and other investments in retirement.
Cons: If the market goes down early in your retirement, it could have a significant impact on how much you can withdraw later.
Best for: Investors who can stomach some risk in the stock market even after they retire.
2. The Bucket Strategy
The bucket strategy for retirement income is also known as time segmentation. Instead of selling your investments equally across the board for income, you instead divide your investments into categories based on when you plan to use the money they generate. For example, if you plan to be retired for 30 years, you may have a near-term bucket designed to provide income for the first third of your retirement, a mid-range bucket for the next third, and a long-term investment bucket for the final third.
The near-term bucket is typically filled with lower-risk investments such as CDs, annuities, bonds or cash, which you don’t have to worry about during market fluctuations. Your longest-range bucket would be filled with riskier investments that have the potential to bring higher rewards over time. Since you won’t be using that money right away, you can weather the ups and downs more easily.
Of course, it’s still important to keep each bucket carefully diversified and to adjust for risk over time. As you enter your final third of retirement, you don’t want to keep all of your money in high-risk investments. Buckets need to be adjusted regularly to stick a careful balance.
Pros: Bucket strategies can help you better understand risk and take market fluctuations in stride.
Cons: There are a lot of moving parts, and you’ll need to pay attention and regularly adjust the buckets over time. This is not a set-it-and-forget it strategy.
Best for: Investors who are engaged in the process and want to feel in control of their risk.
3. The Income Portfolio Strategy
While the first two strategies involved selling off investments to generate income, the income portfolio instead relies on the investments to deliver earnings for you to live on. For example, if you had millions of dollars, you could simply place it in a savings account and live off of the interest without touching a dime of the principal.
Of course, there are other places to put your money than a savings account to deliver income. Creating a bond ladder is one way to create income over time. It’s also possible to buy CDs with staggered maturity dates so you reap the interest over time. Annuities and stocks that pay high dividends are other ways to ensure that you live off your earnings rather than selling your investments.
Pros: When you avoid selling investments, you may have a very stable foundation of money for peace of mind — and for your legacy to your heirs.
Cons: This strategy often requires a big nest egg to be successful.
Best for: Investors with low income needs during retirement and those who have been savings for decades.
4. The Essentials vs. Discretionary Strategy
The essentials vs. discretionary income strategy is also known as a flooring strategy. In this scenario, you carefully divide your wants from your needs during your retirement. The most important goal is to always have enough income for your needs: food, housing, utilities, taxes, health insurance, etc. Because these expenses are non-negotiable, the income you need to pay for them should come from a stable, low-risk source: social security payments would fall into this category, as would any guaranteed pension income, annuities, and bond ladders.
Once you’ve planned for your needs, the rest is the icing. You may plan to travel, indulge in sporting and entertainment, give regularly to charity, or pursue your passions. The funding for these activities comes from riskier investments like stocks or commodities, which will have greater fluctuations over time. The idea is that you can adjust your wants easily, enjoying yourself more in good economic times and tightening your belt in lean times.
Pros: This strategy helps balance risk and reward while providing basic security.
Cons: You need to be willing to deny yourself certain pleasures in an economic downturn.
Best for: People with a flexible outlook who are willing to roll with economic ups and downs.
Next Steps: Turning Your Retirement Savings Into Sustainable Income
If balancing all of these numbers on your own feel overwhelming, we can help. We are happy to assess your current portfolio, analyze your needs, and help you choose an income strategy that works for you. These are complex decisions with many moving parts, and we’re here to help you make sense of it all.
To learn more about maximizing your future retirement income, reach out to us any time for a consultation. We’re ready and waiting to help.
Losing a loved one is always difficult, and the death of a parent can be particularly unsettling. Many people describe the loss of their parents as being orphaned: No matter how old you are or how well established in your life, this major loss will lead you to reevaluate your place in the world.
In addition to strong feelings of grief, losing a parent also means dealing with a mountain of paperwork. As an heir to their estate, you’ll be left to sort out their finances, put their affairs in order, and complete any final wishes about the things they’ve left behind.
From requesting death certificates to preparing a final tax return, there’s a lot to keep track of — it’s completely natural to feel overwhelmed. To help you sort through all the paperwork and keep things organized, we’ve put together this checklist to walk you through the major steps of handling your parent’s finances.
Get Copies of the Will
It’s best to have the will as early as possible, especially if there are instructions about funeral arrangements included in it. This will help you planning your parent’s final resting place and will be necessary for appropriately dividing the estate among heirs in the coming weeks and months.
Gather Identifying Documents
As you deal with various financial entities, you’ll need to prove your parent’s identity. To do this, you will need:
- Birth certificates (for your parent and their children)
- Social Security cards
- Marriage certificates
- Divorce paperwork
- Military discharge papers
You may need some or all of these identifying documents for your other deceased parent and any of your parent’s heirs as well.
Get Copies of the Death Certificate
Most people are surprised at how many copies they will need of the death certificate to send to various financial institutions. Many experts recommend ordering up to 20 copies so you’ll have what you need and avoid the hassle of having to order more. You can usually order these from the funeral director or from your local Board of Health.
Inform Your Parent’s Employer
If your parent was still working, contact human resources to inform them of their death. Ask for information about benefits, which may include additional life insurance, health insurance, and retirement plan information.
Inform the Social Security Office
If your parent received Social Security, you’ll need to call to let them know your parent has died. They can help you switch payments to a surviving spouse if necessary and let you know if you or anyone else is eligible for a death benefit.
Inform the Veteran’s Administration
If your parent was a veteran, the VA may offer special funeral arrangements and other benefits, including survivor benefits.
Start the Probate Process
Having your parent’s will is only the first step to dividing their estate. Though a surviving spouse will typically get everything upon the death of one parent, when both are gone, you’ll have to go through probate court to authenticate the will and officially divide the estate’s assets. Each state has different rules and regulations, so working with a lawyer is a good idea.
Tip: If you are named the executor of the estate in the will, keep receipts for your related expenses so you can be reimbursed from the estate.
Settle a Living Trust
If your parent created a living trust instead of a will, you will be able to avoid probate court to divide the assets. Instead, the designated trustee (which could be you, a relative, or a third party) will settle the estate. This involves gathering all the trust’s assets, paying off any bills or debts, and dividing what’s left among the named beneficiaries of the trust.
Gather Financial Paperwork
To resolve your parent’s finances—whether they had a will or a trust—you’ll need information on all their accounts. These may include:
- Bank accounts, such as checking and savings accounts
- IRAs
- Pension account information
- 401(k) or 403(b) retirement plans
- Annuities
- Brokerage investment accounts
- Life insurance policies
- Deeds for other property and assets, such
You’ll also need to gather information about accounts to which they owe money. These may include:
- Tax returns
- Mortgage statements
- Other loans, including student loans, home equity lines of credit, car loans, etc.
- Utility bills for items like cable, electricity, gas or fuel oil, etc.
- Credit card statements
Tip: If you aren’t sure that you know about all of your parent’s accounts, check their mail for the next three to six months to intercept bills and paperwork. You may find it easier to have their mail forwarded to you for convenience.
File a Final Tax Return With the IRS
You will need to file a final tax return for your deceased parent. Keep all of the paperwork you’ve gathered handy for filling that next April, and be on the lookout for W-2 forms and any final tax documents as they become available in January so you can file accurately.
Make Necessary Cancellations
Use the paperwork you’ve gathered as a guide to help you cancel accounts that are no longer necessary. These may include:
- Credit cards
- Lines of credit
- Health insurance
- Auto insurance
- Voter registration
- Memberships to clubs, subscriptions, etc.
- Driver’s license
- Email, social media, and other online accounts
Change or Close Accounts
If you have a surviving parent, you may need to transfer utility bills, mortgage accounts, and other property, assets and bills into their name. Review the financial documents to determine which payments still need to be made and arrange for them to be paid without interruption.
If you do not have a surviving parent, learn how to close accounts that are no longer needed and how to set up payment for debts that must be cleared.
File Claims for Benefits
You’ll need to file a claim to receive life insurance benefits if your parent had a policy. Likewise, you may be eligible for benefits from their retirement accounts, depending on their designated beneficiaries. A professional financial planner can help you file these claims and make the most of these benefits.
Get Professional Help
Depending on the complexity of your parent’s finances, dealing with their final affairs can be a major challenge. A good probate lawyer and knowledgeable financial planner will help you sort through the details and ensure that you don’t miss anything as you complete this process. They will also advocate for you as you work through this difficult process.
If you need help getting your own finances in order, we can help. Reach out any time for advice on how to handle your finances and plan your estate — a gift of peace of mind for yourself and your future heirs in their time of need.
You may not be able to turn back the clock to open your own retirement accounts earlier, but you can set your children and grandchildren up for success with a Roth IRA for kids. Here’s what you need to know.
Compound Interest: Time Is on Your Side
When you invest your money over a longer period of time, you’ll see exponential growth by the time you’re ready to retire—and that’s all courtesy of the magic of compound interest. For a snapshot of its power, think about a $100 per month investment that you make for 50 years. Sitting in a checking account earning no interest at all, you’d have $60,000 at the end of your investment period.
If you earn compound interest on that amount—meaning that every year you earn 5% interest the amount you have saved so far—you’ll earn interest on your interest as well as your principal savings, and your total will skyrocket. With a 5% average annual return compounded annually on our little $100-a-month account, you’d have over $250,000 after 50 years. At a 10% average annual return you would have nearly $1,400,000 after 50 year investing just $100-a-month.
It pays to start early.
Roth IRAs for Children: Tax Free Investing
To get your children or grandchildren started early on investing, you can open a custodial Roth IRA. As the custodian, you will control this account on their behalf until they reach adulthood.
A Roth IRA is ideal for children because of the way its tax advantages are structured. With a Roth, your child contributes post-tax income to the account, up to a maximum of $6,000 per year.
But here’s the thing: Kids don’t earn much money, so they’re unlikely to owe any taxes on their earnings anyway. Dependents are subject to a reduced standard deduction, but it’s still more than $6,000—which means they can max out their Roth IRAs without paying taxes on any of that income.
Ever.
Because the earnings on a Roth IRA are tax-free, your child can reap the benefits of decades of compound interest without ever paying taxes on that money. They won’t be taxed on what goes in, and they won’t be taxed when they take distributions later.
Important Roth Rules for Kids
Like adults, kids must have earned income to contribute to a Roth IRA. For teens, this can be from standard life guarding and burger flipping W-2 jobs. Earned income can also be in the form of money earned for odd jobs like tutoring, babysitting, or even operating a lemonade stand. The key is to make sure you track income from these odd jobs by keeping receipts or a log so you can prove your child actually earned the money—it can’t be a gift from you.
Your child can invest 100% of their earnings up to the maximum of $6,000 per year. If you want to let them keep their money and “give” them the cash to invest in the Roth yourself, that’s fine. As long as the total in the account doesn’t exceed their earnings, the IRS won’t care.
Looking for a great Roth IRA for your kids or grandkids? We’re here to help with all your investment needs, so contact us today.
There’s never been a better time to make sure your finances are in order.
It’s stating the obvious, but we are now all living through a period in history none of us will ever forget — “uncertain times,” indeed. The impact on our families, communities, and the country as whole has been, and will continue to be, profound. It’s a scary time, but there’s one important piece of advice that can see you through the worst:
Focus on the things you can control.
As the old saying goes, “When life gives you lemons, make lemonade.” Today’s economy is a real lemon, but obsessively watching the news and the state of the stock market isn’t going to help. Instead, take a look at what you do have and make the absolute most of it. In this way, you’ll be squeezing maximum value out of your personal finances and positioning yourself for a better tomorrow.
Here is a checklist of action items that you can fine-tune before life speeds back up again. If you’ve never thought about some of these points, that’s okay. Now is the perfect time to get started.
Estate Planning
Most people do this once and forget about it for decades, but your estate planning needs change just as you grow and change over the years. Make sure your current plans still meet your needs.
- Review Your Beneficiaries. This includes your investment accounts, retirement accounts and pensions, bank accounts, and life insurance. Make sure your beneficiary choice and contact information is up to date.
- Review Your Documents. This includes your Last Will and Testament, Power of Attorney, Living Will and perhaps a Living Trust. Are they up to date? If you need to get started on any of these, we can provide resources for you.
- Inform Your Loved Ones. Should something happen to you, do your loved ones know what to do? Where to find your documents? Who to contact? Create a document and provide both digital and hard copies of this important information.
Insurance
If your insurance auto-renews each year, you might not have the correct coverage for your current needs. You also might be overpaying!
- Review Your Coverage. Is your homeowners insurance sufficient? Should you still be carrying collision coverage on an older vehicle? Do you have enough cash on hand to raise your deductible and enjoy premium savings? Ask for new quotes to see how these changes affect your bottom line. This is also a great time to ask for discounts.
- Record Your Belongings. Take pictures or video of your valuables to provide to the insurance company if they are stolen or destroyed. It’s the best way to streamline a claim and make sure you get what you’re entitled to.
- Consider an Umbrella Policy. This extra liability insurance is typically a great value when it comes to protecting yourself from a lawsuit that could ruin you.
- Recalculate Your Life Insurance Needs. Do you have the right amount of life insurance to protect your family? Try a simple calculator to see how much you need, or get in touch for help.
Budgeting
When’s the last time you reviewed your monthly budget? Of course, you don’t want to use the last 30 days of spending as a guide, since many normal spending habits have been forced to change as we practice social distancing.
- Use 2019 Numbers. This will help you get a more accurate view of your typical income and spending. By looking at real numbers, you can see how much you actually spend in different categories and make some adjustments if needed.
- Review Your Auto-Pay Expenses. It’s so easy to forget about old subscriptions and services we no longer need — but that we still pay for via auto deduction. Cancel these budget vampires and breathe a sigh of relief.
Taxes
Recent tax law and IRS rule changes mean that you might be missing out on some savings.
- Consider Converting to a Roth IRA. With many IRAs being down in value, converting a Traditional IRA to a tax-free growth Roth IRA may save money on taxes. We’re happy to discuss your options to help you make the most of your retirement.
- Set Up IRA Contributions: See if you can increase your contributions to maximize your savings. If you didn’t make 2019 IRA contributions, you can still do so until July 15, thanks to a COVID-related IRS extension.
- Explore Charitable Giving: The CARES Act has expanded deductions for charitable giving this year, so it’s a great time to help worthy organizations. Qualified Charitable Contributions (QCDs) can help you to support causes you believe in using required minimum distributions from retirement accounts.
General Maintenance
With extra time on your hands, it also makes sense to do some general financial housekeeping to make it easier to review your paperwork in the future.
- Update Your Financial Dashboard. If you’re using personal finance software, be sure you’re linked to all your current accounts for accurate tracking and budgeting.
- Trash Old Documents. Be sure to shred those papers to protect sensitive personal information and account numbers.
- Organize Your Financial Files. Get those tax returns, insurance policies, and more into neatly labeled folders for ease of use later.
- Scan and Save Important Documents. If you don’t already have digital versions of your paperwork, take the time to scan them and create a digital filing cabinet now.
Some thoughts about planning for the future.
With your financial life organized and streamlined, you should feel much better about things. You have all of your information at your fingertips, and that makes it easier than ever to make some smart choices about the future.
If you’d like to talk about your investment options and financial planning needs, we’re always here to help. We know it’s a stressful time, and we pledge to do our best to provide clarity, transparency, and advice that will help you make your best moves in these difficult times.
Please reach out if you’d like more help with financial planning — we’ll be standing by!
In the meantime, stay healthy, safe and sane — and try to enjoy the lemonade you’ve worked to create out of this situation.
For long-term investors, it’s important to focus on tried-and-true disciplines that have worked over time more than what the stock market is currently doing or what the talking heads predict the market will do. Rebalancing is one such discipline that can potentially reduce risk and increase long term performance, and may also help reduce some of the worry that accompanies times of increased market volatility.
What is Rebalancing?
Rebalancing is the process of realigning the weightings of a portfolio to get back to a target asset allocation. It involves periodically buying assets that have decreased in value and selling assets that have increased in value. This discipline is intended to cause investors to buy low and sell high with the goal of maintaining an original desired level of asset allocation.
The figure below shows a target allocation with equal weighting into four different Asset Classes. If any one asset class moves above or below a predetermined percentage (ex. 3%, 5%, 10%) of its target allocations, it’s time to rebalance.
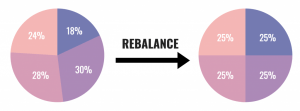
It May Feel Counterintuitive to Buy Low and Sell High
In times of market uncertainty and poor investment performance, selling better performing assets and buying more of the underperforming assets in your portfolio may seem counterintuitive. However, market corrections and deep bear markets represent rebalancing opportunities to increase ownership into positions that have experienced a significant drop in price. For example, if you were happy to buy an investment at a particular price but then the price drops 15%, 20% or more, your first instinct might be to stop the bleeding and sell. However, if you do that you’ve now locked in your loss. Setting up rules for when to rebalance before the market declines may save you from making the typical investor mistake of buying high and selling low.
When to Rebalance?
There is no “perfect” time to rebalance. If you want to take a disciplined approach that removes emotion, consider rebalancing every time your IRA, 401k, TSP or other investment account drops or increases in increments of 3%, 5% or 10% in value. The percentage you select isn’t as important as committing to rebalancing when your reach the threshold. A variation of this method is to rebalance anytime one or more of the funds is 3% or greater outside of it’s target allocation. Alternatively, you can use one of the broad market indexes as an indicator of a good time to rebalance. Hypothetically if the S&P 500 drops 10%, you should see this as a time to buy low and sell high instead of panicking. Buy shares of investments when they are down so you will have more ownership if the investment recovers.
The figure below shows an example of when to rebalance and take advantage while others may be panicking and making mistakes.
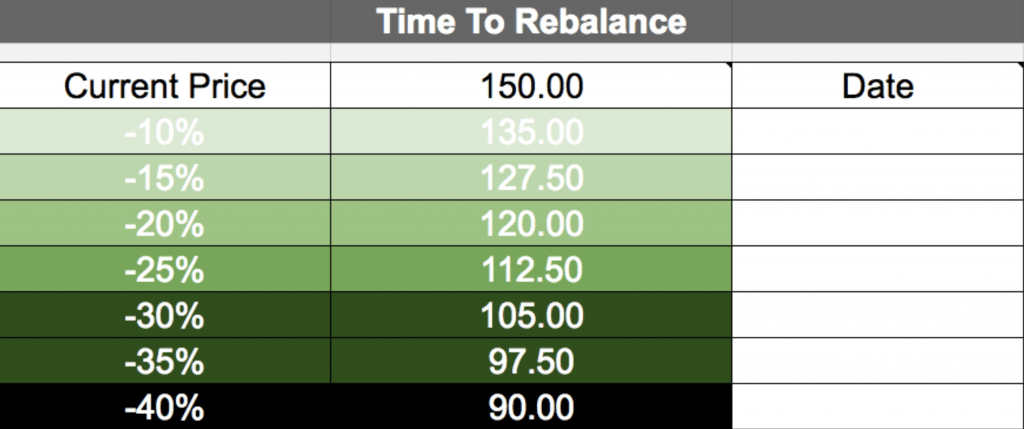
Simple and Actionable
Imagine how empowering it would be to have a simple, actionable plan in place if the stock market drops 10%, 15%, 20% or more that could actually help your investments long term. Consider letting your portfolio tell you when to take action and rebalance, not a media personality whose primary job may be to keep you afraid and tuned in for higher ratings.
Next Steps
- Establish the appropriate asset allocation for your personal risk tolerance and time horizon (when you need to use the money).
- Rebalance (buy low, sell high) your asset allocation established using one of the methods mentioned above.
- Update step one every few years.
Good luck!
Rebalancing is a strategy that can’t guarantee against a loss or better portfolio performance and could result from missing out on additional gains from appreciated assets. This is not intended to be financial advice. Please consult an investment professional on any strategy or your individual situation. Examples are for illustrative purposes only. Past Performance doesn’t guarantee future results.








